Uveitis Treatment
“Uveitis” is a broad term that is used to describe inflammation affecting the eyes. Uveitis can be acute, occurring in symptomatic flare-ups with periods of relative calm in between. It can also be chronic, causing inflammation over time without any obvious symptoms.
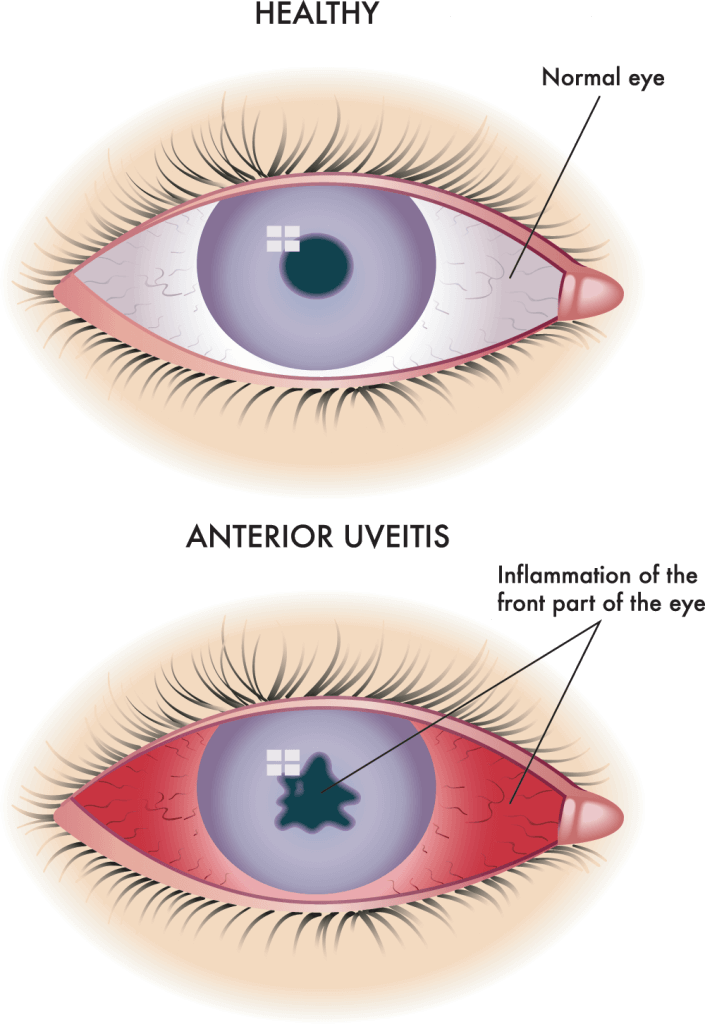
Uveitis can be classified by the different parts of the eye that are affected:
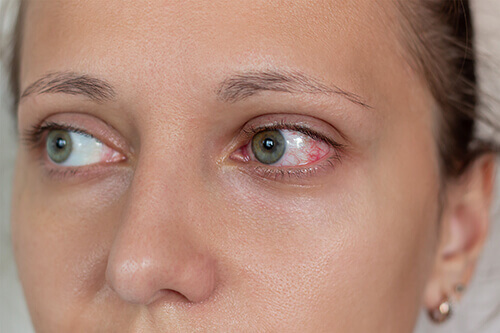
- Anterior uveitis affects the front part of the eye. Symptoms of anterior uveitis may include redness, light sensitivity and eye pain.
- Intermediate uveitis affects the middle part of the eye. Symptoms of intermediate uveitis may include floaters or cloudy vision.
- Posterior uveitis affects the back of the eye. Symptoms of posterior uveitis may include flashes, flickering, decreased vision, or new blind spots.
- Panuveitis affects all layers of the eye. Symptoms of panuveitis can be quite varied.
- Scleritis affects the sclera, or outer collagenous wall, of the eye. Symptoms of scleritis include redness, tenderness to touch, and a deep, boring eye pain that can wake you up from your sleep.
- Retinal vasculitis affects the blood vessels inside of the eye. Retinal vasculitis is not typically painful. Symptoms of retinal vasculitis can include decreased vision, floaters, flickering, or blind spots.
Uveitis can be either infectious or noninfectious. Infectious causes of uveitis may be from viruses, bacteria, parasites, or fungi.
Examples of organisms that can cause infectious uveitis to include:
- herpes virus
- shingles
- toxoplasmosis
- syphilis
- tuberculosis
Some cases of noninfectious uveitis may be related to systemic autoimmune disorders, such as:
- sarcoidosis
- inflammatory bowel disease
- rheumatoid arthritis
- multiple sclerosis
- lupus
- ankylosing spondylitis, or other diseases.
In other cases, they can be related to systemic medications. In about half of all noninfectious uveitis cases, the cause is idiopathic, or unknown. Your doctor may request for you to have bloodwork or imaging performed to look for systemic causes of your uveitis.
Treatment
The treatment of uveitis depends on the cause of the condition.
In the case of infection, you may be required to take medications directed toward eradicating the infection.
For noninfectious causes of uveitis, treatment options may include steroid eye drops, local steroid injections, systemic steroids, or systemic immunosuppressive therapy.
Uveitis specialists often coordinate with other doctors including rheumatologists, neurologists, pulmonologists, cardiologists, and infectious disease doctors.
If you have uveitis, it is important to follow up with your uveitis specialist regularly, since untreated ocular inflammation can result in permanent damage to the eye and irreversible vision loss.
